เครื่องกัดซีเอ็นซี (เครื่องกัดควบคุมเชิงตัวเลขด้วยคอมพิวเตอร์) เป็นเครื่องมือตัดขั้นสูงที่ใช้ระบบควบคุมด้วยคอมพิวเตอร์เพื่อตัดและขึ้นรูปวัสดุอย่างแม่นยำ ต่างจากเครื่องกัดแบบดั้งเดิม เครื่องกัดซีเอ็นซีทำงานตามคำสั่งที่ตั้งโปรแกรมไว้เพื่อผลิตชิ้นส่วนที่ซับซ้อนด้วยความแม่นยำและความสม่ำเสมอที่ยอดเยี่ยม
บทความนี้จะอธิบายนิยามและหลักการทำงานของเครื่องกัดซีเอ็นซี พร้อมอธิบายวิธีการทำงานของเครื่อง ส่วนประกอบหลัก และการใช้งานทั่วไปในการผลิตสมัยใหม่ ไม่ว่าคุณจะเป็นมือใหม่หรือผู้เชี่ยวชาญในอุตสาหกรรม คู่มือนี้จะช่วยให้คุณเข้าใจสาระสำคัญของเครื่องกัดซีเอ็นซีและบทบาทของมันในการผลิตที่แม่นยำ
เครื่องกัดซีเอ็นซี (CNC Milling Machine) หรือที่ย่อมาจาก Computer Numerical Control Milling Machine เป็นอุปกรณ์ตัดเฉือนชนิดหนึ่งที่ตัดวัสดุออกจากชิ้นงานด้วยความแม่นยำสูงโดยใช้เครื่องมือตัดแบบหมุน ส่วน "CNC" หมายถึงการเคลื่อนที่ทุกอย่างของเครื่องจักร เช่น การหมุนแกนหมุน การเปลี่ยนเครื่องมือ และการวางตำแหน่งโต๊ะ จะถูกควบคุมด้วยโปรแกรมคอมพิวเตอร์แทนการควบคุมด้วยมือ
ต่างจากเครื่องกัดแบบดั้งเดิมที่ต้องอาศัยทักษะของผู้ปฏิบัติงานอย่างมาก เครื่องกัด CNC ปฏิบัติตามคำสั่งดิจิทัลที่ตั้งไว้ล่วงหน้า ซึ่งสร้างจากซอฟต์แวร์ CAD (การออกแบบด้วยคอมพิวเตอร์) และ CAM (การผลิตด้วยคอมพิวเตอร์) ซึ่งช่วยให้สามารถผลิตรูปทรงที่ซับซ้อน มีค่าความคลาดเคลื่อนที่แคบ และให้ผลลัพธ์ที่ทำซ้ำได้อย่างสม่ำเสมอ
ในการผลิตที่ทันสมัย เครื่องกัดซีเอ็นซี ถูกนำมาใช้อย่างแพร่หลายในการผลิตชิ้นส่วนที่ทำจากโลหะ พลาสติก หรือวัสดุคอมโพสิต ความสามารถในการผสานความแม่นยำ ความเร็ว และระบบอัตโนมัติเข้าด้วยกัน ทำให้ชิ้นส่วนเหล่านี้มีความสำคัญอย่างยิ่งในอุตสาหกรรมต่างๆ เช่น การบินและอวกาศ ยานยนต์ การแพทย์ และวิศวกรรมแม่นยำ
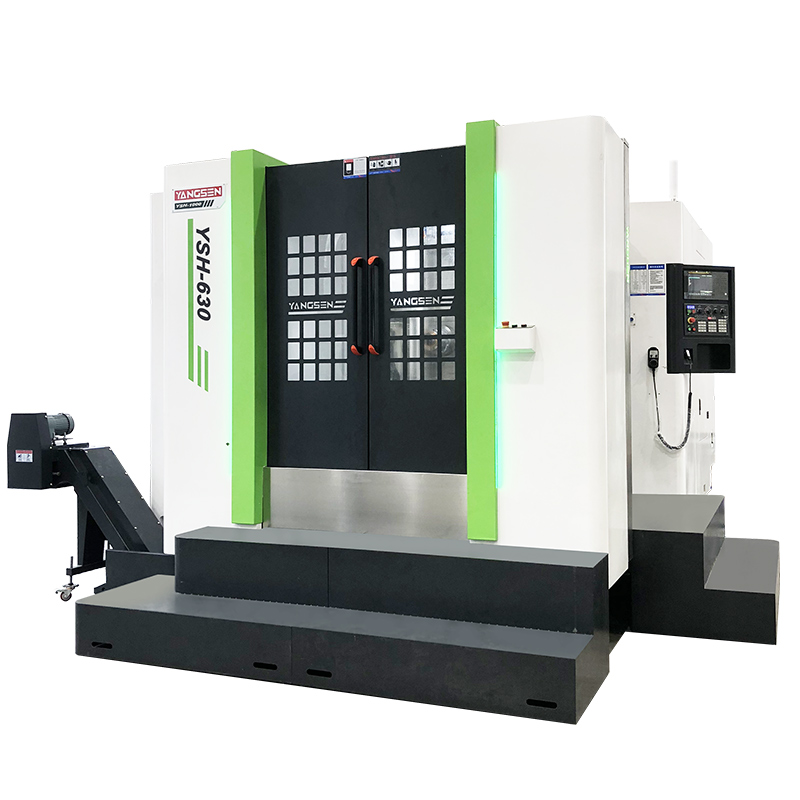

หลักการทำงานของเครื่องกัดซีเอ็นซี (CNC Mill) ยึดหลักความแม่นยำที่ควบคุมด้วยคอมพิวเตอร์ กระบวนการตัดเฉือนทุกขั้นตอนเริ่มต้นด้วยการออกแบบดิจิทัลที่สร้างขึ้นในซอฟต์แวร์ CAD จากนั้นการออกแบบนี้จะถูกแปลงเป็นโปรแกรม CAM ซึ่งจะสร้างชุดคำสั่ง G-code ซึ่งเป็นภาษาที่บอกเครื่อง CNC อย่างชัดเจนว่าต้องเคลื่อนย้าย ตัด และขึ้นรูปวัสดุอย่างไร
ในระหว่างการทำงาน ตัวควบคุม CNC จะอ่านรหัสเหล่านี้และสั่งให้แกนหมุนและเครื่องมือตัดของเครื่องจักรเคลื่อนที่ไปตามแกนต่างๆ (โดยทั่วไปคือแกน X, Y และ Z) แกนหมุนจะหมุนเครื่องมือตัดด้วยความเร็วสูง ขณะที่โต๊ะหรือชิ้นงานจะเคลื่อนที่ตามเพื่อกำจัดวัสดุทีละชั้น การประสานงานอัตโนมัตินี้ช่วยให้โรงสีสามารถตัดได้อย่างแม่นยำสูงสุดและสร้างรูปทรงที่ซับซ้อน ซึ่งยากหรือเป็นไปไม่ได้ที่จะทำด้วยมือ
วงจรการกัด CNC ทั่วไปประกอบด้วยหลายขั้นตอน:
การออกแบบและการเขียนโปรแกรม – สร้างแบบจำลองชิ้นส่วนและสร้าง G-code
การตั้งค่า – ติดตั้งชิ้นงานและเลือกเครื่องมือตัดที่เหมาะสม
การตัดเฉือน – ระบบ CNC จะดำเนินการเคลื่อนไหวตามโปรแกรมสำหรับการกำจัดวัสดุ
การตรวจสอบ – วัดและยืนยันขนาดและคุณภาพของพื้นผิวของชิ้นส่วนสำเร็จรูป
กระบวนการควบคุมแบบทีละขั้นตอนนี้ช่วยให้มั่นใจถึงความแม่นยำสูง ความสามารถในการทำซ้ำ และประสิทธิภาพ ทำให้การกัด CNC เป็นเทคโนโลยีหลักในการผลิตและการสร้างต้นแบบขั้นสูง
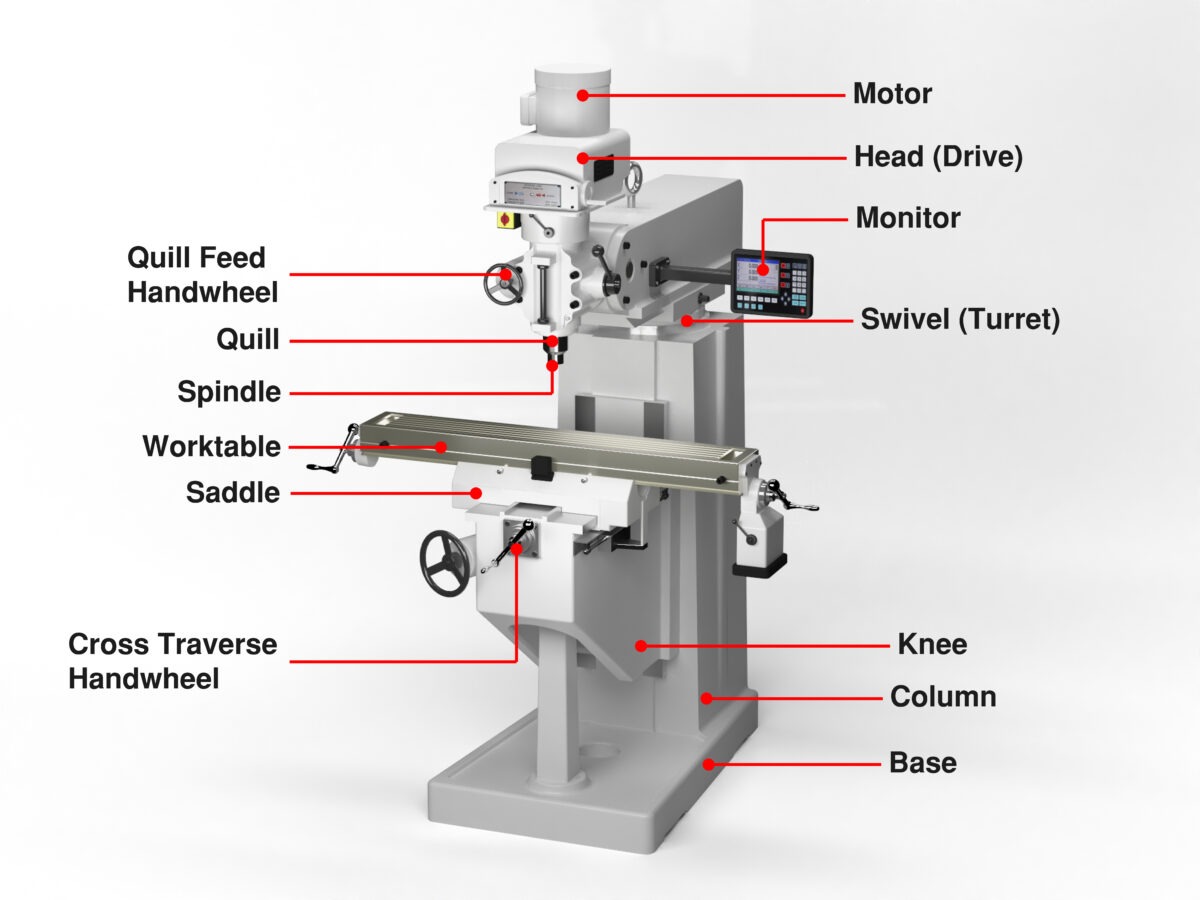
เครื่องกัดซีเอ็นซีประกอบด้วยส่วนประกอบสำคัญหลายชิ้นที่ทำงานร่วมกันเพื่อให้มั่นใจถึงประสิทธิภาพการตัดเฉือนที่แม่นยำและเสถียร การทำความเข้าใจส่วนประกอบเหล่านี้จะช่วยให้ผู้ปฏิบัติงานและวิศวกรสามารถเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพและความแม่นยำของเครื่องจักรได้สูงสุด
แกนหมุน – แกนหมุนคือหัวใจสำคัญของเครื่องกัดซีเอ็นซี ทำหน้าที่ยึดและหมุนเครื่องมือตัดด้วยความเร็วสูง มอบกำลังที่จำเป็นสำหรับการกำจัดวัสดุ ความเร็ว ความเสถียร และความแม่นยำของแกนหมุนส่งผลโดยตรงต่อคุณภาพการตัดเฉือน
ที่จับเครื่องมือและตัวเปลี่ยนเครื่องมือ – ที่จับเครื่องมือจะเชื่อมต่อเครื่องมือตัดเข้ากับแกนหมุน ในขณะที่ตัวเปลี่ยนเครื่องมืออัตโนมัติช่วยให้เครื่องจักรสามารถสลับเครื่องมือระหว่างการทำงานได้โดยไม่ต้องมีการแทรกแซงจากมือ ช่วยเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพและความยืดหยุ่นในการผลิต
โต๊ะทำงาน – โต๊ะรองรับและจัดตำแหน่งชิ้นงาน เคลื่อนที่ไปตามแกน X และ Y ช่วยให้วางตำแหน่งได้อย่างแม่นยำระหว่างการตัด
มอเตอร์เซอร์โวและระบบขับเคลื่อน – ส่วนประกอบเหล่านี้ควบคุมการเคลื่อนที่ของแกนหมุนและโต๊ะ ช่วยให้การเคลื่อนที่ราบรื่นและแม่นยำตามแกนแต่ละแกนตามคำสั่งที่ตั้งโปรแกรมไว้
ตัวควบคุม CNC – มักเรียกกันว่า “สมอง” ของเครื่องจักร ตัวควบคุมจะตีความคำสั่ง G-code และประสานงานการเคลื่อนไหวทั้งหมดของแกนหมุน แกน และตัวเปลี่ยนเครื่องมือ
ระบบกำจัดน้ำหล่อเย็นและเศษโลหะ – น้ำหล่อเย็นช่วยรักษาอุณหภูมิในพื้นที่ตัดให้คงที่ ป้องกันการสึกหรอของเครื่องมือ ขณะเดียวกัน ระบบกำจัดเศษโลหะยังช่วยขจัดเศษโลหะออก เพื่อให้สภาพแวดล้อมการทำงานสะอาดและมีประสิทธิภาพ
ส่วนประกอบเหล่านี้เมื่อนำมารวมกันจะทำให้เครื่องกัด CNC สามารถกลึงชิ้นงานที่มีความเร็วสูงและแม่นยำสูงได้ สำหรับการใช้งานในอุตสาหกรรมที่หลากหลาย
เครื่องกัดซีเอ็นซีมีหลายประเภท แต่ละประเภทออกแบบมาเพื่อการใช้งานเฉพาะและระดับความแม่นยำ การทำความเข้าใจประเภทเหล่านี้จะช่วยให้ผู้ผลิตเลือกเครื่องจักรที่เหมาะสมกับความต้องการในการผลิตของตนได้
แกนหมุนถูกวางแนวตั้งเพื่อตัดลงบนชิ้นงาน
เหมาะสำหรับงานกลึงทั่วไปและชิ้นส่วนขนาดเล็กถึงขนาดกลาง
นิยมใช้ในอุตสาหกรรมต่างๆ เช่น ยานยนต์ อิเล็กทรอนิกส์ และการสร้างต้นแบบ
แกนหมุนอยู่ในแนวนอน ช่วยให้สามารถตัดชิ้นงานได้หลายด้าน
เหมาะสำหรับงานเครื่องจักรกลหนักและการผลิตปริมาณมาก
ช่วยให้ขจัดเศษวัสดุได้ดีขึ้นและมีเสถียรภาพมากขึ้นสำหรับชิ้นงานขนาดใหญ่
สามารถเคลื่อนย้ายแกนหมุนและโต๊ะได้พร้อมกัน 5 แกน
เหมาะอย่างยิ่งสำหรับรูปทรงเรขาคณิตที่ซับซ้อน ชิ้นส่วนอากาศยาน และการทำแม่พิมพ์
ลดเวลาในการตั้งค่าและปรับปรุงความแม่นยำในการตัดเฉือนสำหรับชิ้นส่วนที่ซับซ้อน
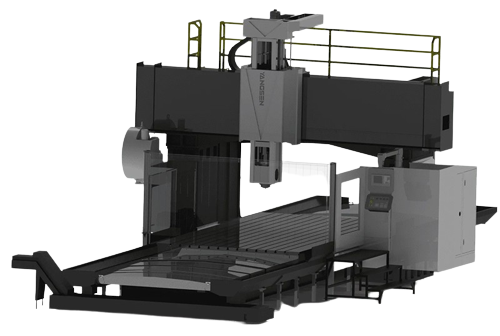
เครื่องจักรขนาดใหญ่ที่มีโครงสร้างคล้ายสะพาน เหมาะสำหรับชิ้นงานขนาดใหญ่มาก
ใช้ในอุตสาหกรรมต่างๆ เช่น การต่อเรือ อวกาศ และเครื่องจักรกลหนัก
เครื่องจักรขนาดเล็กสำหรับงานเบาและงานแม่นยำ
มักพบในสถาบันการศึกษา ห้องปฏิบัติการขนาดเล็ก และห้องปฏิบัติการสร้างต้นแบบ
เครื่องกัดซีเอ็นซีถูกนำมาใช้กันอย่างแพร่หลายในหลายอุตสาหกรรม เนื่องจากมีความแม่นยำ ประสิทธิภาพ และความยืดหยุ่น การใช้งานหลักๆ ได้แก่:
การผลิตใบพัดกังหัน, ตัวเรือนเครื่องยนต์ และชิ้นส่วนโครงสร้าง
ความแม่นยำสูงและความคลาดเคลื่อนที่เข้มงวดเป็นสิ่งสำคัญต่อความปลอดภัยและประสิทธิภาพการทำงาน
ผลิตแม่พิมพ์, กระปุกเกียร์, ชิ้นส่วนเครื่องยนต์ และส่วนประกอบที่กำหนดเอง
โรงสี CNC ช่วยเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพและรับประกันคุณภาพที่สม่ำเสมอสำหรับการผลิตปริมาณมาก
การประดิษฐ์ชิ้นส่วนปลูกถ่าย เครื่องมือผ่าตัด และอุปกรณ์เทียม
ช่วยให้มีรูปทรงเรขาคณิตที่ซับซ้อนและขนาดที่แม่นยำซึ่งจำเป็นต่อความปลอดภัยของผู้ป่วย
ผลิตตู้หุ้ม, แผงระบายความร้อน, ขั้วต่อ และแผงวงจร
ชิ้นส่วนขนาดเล็กและมีรายละเอียดต้องใช้ความแม่นยำที่การกัด CNC ให้มา
การสร้างแม่พิมพ์ แม่พิมพ์และอุปกรณ์จับยึดที่มีความแม่นยำสำหรับการผลิต
การกัด CNC ช่วยให้รอบการผลิตเร็วขึ้นด้วยการปรับด้วยมือเพียงเล็กน้อย
ผลิตต้นแบบอย่างรวดเร็วสำหรับการทดสอบและการตรวจสอบการออกแบบ
ช่วยให้สามารถทำซ้ำและปรับเปลี่ยนได้อย่างรวดเร็วก่อนการผลิตจำนวนมาก
การใช้ประโยชน์จากการกัด CNC ทำให้บริษัทต่างๆ ในอุตสาหกรรมเหล่านี้สามารถบรรลุความแม่นยำที่สูงขึ้น ลดข้อผิดพลาด และเพิ่มผลผลิต ทำให้กลายเป็นเทคโนโลยีที่จำเป็นในการผลิตสมัยใหม่
เครื่องกัดซีเอ็นซีมีความแม่นยำสูงและความสามารถในการทำซ้ำได้ ช่วยให้ผู้ผลิตสามารถผลิตชิ้นส่วนที่มีคุณภาพสม่ำเสมอ ความแม่นยำในระดับนี้เป็นสิ่งจำเป็นสำหรับอุตสาหกรรมต่างๆ เช่น การบินและอวกาศ ยานยนต์ และอุปกรณ์ทางการแพทย์ ซึ่งแม้แต่ความคลาดเคลื่อนเพียงเล็กน้อยก็อาจก่อให้เกิดปัญหาใหญ่ได้
ระบบอัตโนมัติในการกัด CNC ช่วยเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพและลดข้อผิดพลาดของมนุษย์ได้อย่างมาก การกัดแบบหลายแกนช่วยให้สามารถสร้างรูปทรงที่ซับซ้อนได้โดยใช้การตั้งค่าน้อยลง ช่วยประหยัดเวลาและต้นทุนแรงงาน พร้อมทั้งรักษาผลลัพธ์ที่สม่ำเสมอตลอดกระบวนการผลิต
นอกจากนี้ เครื่องกัด CNC ยังมีความอเนกประสงค์สูง สามารถทำงานกับวัสดุได้หลากหลายประเภท ทั้งโลหะ พลาสติก และวัสดุผสม เหมาะสำหรับทั้งการผลิตต้นแบบและการผลิตขนาดใหญ่ ด้วยการผสมผสานความเร็ว ความยืดหยุ่น และความน่าเชื่อถือ เพื่อเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพการผลิตโดยรวม
คุณสมบัติ | การกัดซีเอ็นซี | การกลึง CNC |
การเคลื่อนไหว | เครื่องมือหมุน ชิ้นงานเคลื่อนที่ | ชิ้นงานหมุน เครื่องมืออยู่นิ่ง |
ชิ้นส่วนทั่วไป | รูปทรงที่ซับซ้อน พื้นผิวเรียบ | ชิ้นส่วนทรงกระบอกหรือสมมาตร |
ขวาน | โดยทั่วไปมี 3–5 แกน | โดยทั่วไปมี 2–3 แกน |
ความซับซ้อนในการตั้งค่า | ปานกลางถึงสูง | ปานกลาง |
กรณีการใช้งานที่ดีที่สุด | ชิ้นส่วนหลายด้านและมีรายละเอียด | ชิ้นส่วนทรงกลม ผลิตปริมาณมาก |
การเลือกเครื่องกัดซีเอ็นซีที่เหมาะสมขึ้นอยู่กับปัจจัยสำคัญหลายประการ รวมถึงความต้องการด้านการผลิต งบประมาณ และวัสดุที่ใช้ อันดับแรก ให้พิจารณาประเภทของเครื่องกัด ได้แก่ แนวตั้ง แนวนอน หรือ 5 แกน โดยพิจารณาจากความซับซ้อนของชิ้นส่วนและความแม่นยำที่ต้องการ เครื่องกัดแนวตั้งมีความอเนกประสงค์และเหมาะสำหรับการตัดเฉือนทั่วไป ในขณะที่เครื่องกัดแนวนอนและ 5 แกนเหมาะสำหรับการจัดการชิ้นส่วนขนาดใหญ่หรือซับซ้อนกว่า
ขั้นต่อไป ให้ประเมินข้อมูลจำเพาะของเครื่องจักร เช่น ความเร็วแกนหมุน ระยะเคลื่อนที่ของแกน ขนาดโต๊ะ และความสามารถในการรับน้ำหนัก ปัจจัยเหล่านี้กำหนดขนาดของชิ้นงานที่คุณสามารถจัดการ วัสดุที่คุณสามารถกัด และประสิทธิภาพการผลิตโดยรวม สำหรับชิ้นส่วนที่มีปริมาณมากหรือชิ้นส่วนที่ต้องการความแม่นยำสูง การลงทุนในเครื่องจักรที่มีหลายแกนและมีความแข็งแกร่งสูงจะช่วยให้มั่นใจได้ถึงประสิทธิภาพและความสามารถในการทำซ้ำที่ดีขึ้น
สุดท้ายนี้ ควรพิจารณาความเข้ากันได้ของซอฟต์แวร์ การสนับสนุน และการบำรุงรักษา ตรวจสอบให้แน่ใจว่าตัวควบคุม CNC สามารถใช้งานร่วมกับซอฟต์แวร์ CAD/CAM ของคุณได้ และผู้ผลิตให้การสนับสนุนทางเทคนิคและอะไหล่ที่เชื่อถือได้ เครื่องจักรที่ได้รับการสนับสนุนอย่างดีจะช่วยลดระยะเวลาหยุดทำงานและต้นทุนระยะยาว การประเมินปัจจัยเหล่านี้อย่างรอบคอบจะช่วยให้คุณเลือกเครื่องกัด CNC ที่ให้ผลผลิต คุณภาพ และผลตอบแทนจากการลงทุนสูงสุด
การบำรุงรักษาที่เหมาะสมและการใช้งานอย่างปลอดภัยเป็นสิ่งสำคัญอย่างยิ่งต่ออายุการใช้งานและประสิทธิภาพของเครื่องกัดซีเอ็นซี การทำความสะอาดและหล่อลื่นชิ้นส่วนที่เคลื่อนไหวเป็นประจำช่วยป้องกันการสึกหรอและรักษาความแม่นยำ ขณะเดียวกัน การตรวจสอบตัวจับยึดเครื่องมือ แกนหมุน และโต๊ะทำงาน ช่วยให้มั่นใจได้ว่าการตัดเฉือนจะมีเสถียรภาพและแม่นยำ
ผู้ปฏิบัติงานควรตรวจสอบการสึกหรอของเครื่องมือและการสอบเทียบเครื่องจักรเพื่อหลีกเลี่ยงข้อบกพร่องและรักษาคุณภาพให้คงที่ การใช้เครื่องมือตัดที่ถูกต้องและเปลี่ยนชิ้นส่วนที่สึกหรอตามกำหนดเวลาจะช่วยป้องกันความเสียหายต่อทั้งเครื่องจักรและชิ้นงาน
ความปลอดภัยก็สำคัญไม่แพ้กัน ปฏิบัติตามขั้นตอนการปฏิบัติงานมาตรฐาน สวมใส่อุปกรณ์ป้องกันส่วนบุคคลที่เหมาะสม และตรวจสอบให้แน่ใจว่าระบบหยุดฉุกเฉินและการ์ดป้องกันของเครื่องจักรทำงานได้ การปฏิบัติตามตารางการบำรุงรักษาและแนวทางด้านความปลอดภัยไม่เพียงแต่ช่วยยืดอายุการใช้งานของเครื่องจักรเท่านั้น แต่ยังช่วยให้มั่นใจได้ถึงประสิทธิภาพ ความน่าเชื่อถือ และปลอดภัยในการผลิตอีกด้วย
การทำความเข้าใจนิยามและหลักการทำงานของเครื่องกัด CNC ถือเป็นสิ่งสำคัญอย่างยิ่งสำหรับทุกคนที่เกี่ยวข้องกับการผลิตสมัยใหม่ เครื่องกัด CNC ผสานความแม่นยำ ระบบอัตโนมัติ และความหลากหลาย เพื่อผลิตชิ้นส่วนคุณภาพสูงอย่างมีประสิทธิภาพ ทำให้เครื่องกัด CNC กลายเป็นสิ่งที่ขาดไม่ได้ในอุตสาหกรรมต่างๆ เช่น อวกาศ ยานยนต์ การแพทย์ และอิเล็กทรอนิกส์
การเลือกเครื่องจักรที่เหมาะสม การบำรุงรักษาอย่างเหมาะสม และการปฏิบัติตามแนวทางปฏิบัติการใช้งานที่ปลอดภัย ช่วยให้มั่นใจได้ถึงประสิทธิภาพที่สม่ำเสมอและความน่าเชื่อถือในระยะยาว สำหรับธุรกิจที่ต้องการเพิ่มผลผลิตและลดข้อผิดพลาดในการผลิต การลงทุนในโซลูชันการกัด CNC คุณภาพสูงถือเป็นการตัดสินใจเชิงกลยุทธ์